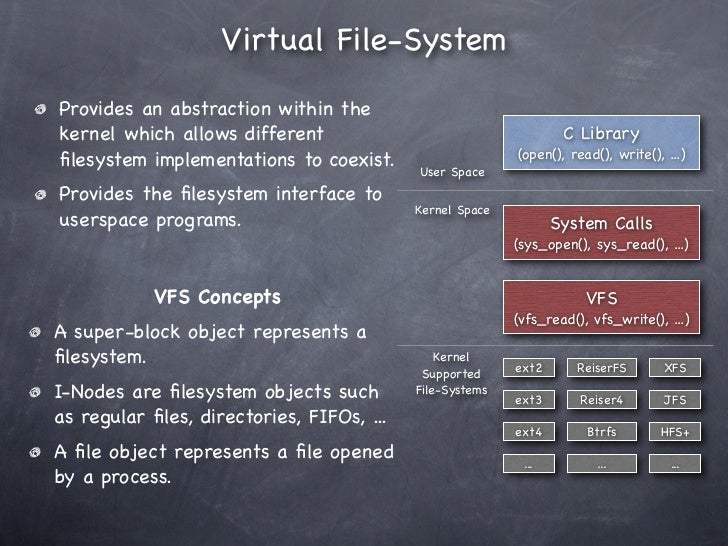
When layered on top of Ext4 compared to native Ext4. We used a wide variety of micro- and macro-workloads, and different hardware using basic and optimized config-urations of FUSE. We found that depending on the work-load and hardware, FUSE can perform as well as Ext4, but in the worst cases can be 3 slower. Fuse box diagram (location and assignment of electrical fuses and relays) for Jeep Wrangler (TJ; 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006). IGN 1 Relay – SBA Fuse, ETC/ECM Fuse, PCM 1 Fuse, INJ 1 Fuse, INJ 2 Fuse PCM 1 15A Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Mass Air Flow (MFS) Sensor. Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Purge Solenoid, Fuel Composition Sensor, Secondary Fuel Pump Relay ETC/ECM 15A Throttle Actuator Control (TAC) INJ 1 15A Fuel Injectors-Odd-Numbered. What is FUSE?¶ FUSE is a userspace filesystem framework. It consists of a kernel module (fuse.ko), a userspace library (libfuse.) and a mount utility (fusermount). One of the most important features of FUSE is allowing secure, non-privileged mounts. This opens up new possibilities for the use of filesystems.
Translation(s): English - Français - Italiano - 简体中文
From Wikipedia:
In computing, a file system or filesystem (often abbreviated to fs), controls how data is stored and retrieved. Without a file system, information placed in a storage medium would be one large body of data with no way to tell where one piece of information stops and the next begins. A file system separates the data into pieces and gives each piece a name. Each group of data is called a 'file'.
There are many different kinds of file systems. Each one has different structure and logic, properties of speed, flexibility, security, size and more.
Files and directories themselves are placed on top of the file system, therefore it is common to refer to the file/directory structure itself as 'file system'. On GNU/Linux, the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard defines the naming scheme and hierarchy between files and directories themselves.
File systems usually sit on top of hard disk partitions or LVM volumes. In Debian, ext4 is the default file system for new installations.
GNU/Linux can be installed on any filesystem that supports some special constructs (file permissions, symbolic links and device files).
Many file systems are journaling, meaning they are able to prevent data loss on system crashes or power failures.
Contents
Mounting a filesystem
In GNU/Linux the contents of a filesystem can be made available under a directory, by mounting the filesystem over the directory. Here are some ways to mount a filesystem:
The mount command. For example mount /dev/sdd1 /mn/ would make contents of the first partition of the /dev/sdd disk device, available in the /mnt/ directory.
Editing the fstab file
Filesystems available in Debian Linux kernel
Note0: Debian HURD and Debian kFreeBSD have other file systems.
Note1: the Features list are incomplete at this time.
Note2: This table is uptodate as of 2.6.28 kernel.
Filesystem name | Features? | Documentation(s) | Description | Distributions |
File systems often used as linux system partition | ||||
ext4 | R | (default filesystem in Debian) Fourth Extended Filesystem with extents | >= Squeeze | |
ext2 | RS | kDoc, WPedia | Second Extended Filesystem | All? |
ext3 | RS | kDoc, WPedia | Second Extended Filesystem with journaling extensions | All? |
ext4dev | R | Fourth Extended Filesystem with extents | Etch-n-Half ~ Lenny | |
jfs | R | The Journaled Filesystem (JFS) | All? | |
xfs | R | SGI XFS Filesystem | All? | |
reiserfs | R | ReiserFS journaled filesystem | All? | |
Other File systems | ||||
9p | Plan 9 9p remote filesystem protocol | All? | ||
adfs | Acorn (and Risc OS) Advanced Disc Filing System | All? | ||
affs | I | Amiga filesystem support for Linux | All? | |
kafs | N | AFS Client File System | All? | |
autofs4 | Auto-mount filesystems. See autofs | All? | ||
autofs | Auto-mount filesystems. See autofs | All? | ||
befs | I | BeOS File System (BeFS) driver | All? | |
bfs | I | SCO UnixWare BFS filesystem for Linux | All? | |
btrfs | RS | B-Tree filesystem | >= Jessie | |
cifs | N I | VFS to access servers complying with the SNIA CIFS Specification e.g. Samba and Windows | All? | |
coda | Coda Distributed File System VFS interface | All? | ||
configfs | Simple RAM filesystem for user driven kernel subsystem configuration. | All? | ||
cramfs | cram a filesystem onto a small ROM | All? | ||
dlm | Distributed Lock Manager | All? | ||
ecryptfs | eCryptfs | All? | ||
efs | SGI EFS, Extent File System (Irix <0.6) | All? | ||
fat | I | MS & DR DOS FAT filesystem | All? | |
freevxfs | Veritas Filesystem (VxFS) driver | All? | ||
fuse | Filesystem in Userspace (backend for various filesystems) | All? | ||
gfs2 | N | Global File System | All? | |
hfs | I | Macintosh HFS Filesystem | All? | |
hfsplus | I | HFSPlus / Extended Macintosh Filesystem | All? | |
hpfs | I | High Performance Filesys (OS/2's HPFS) | All? | |
isofs | CD | CD/DVD filesystem (ISO-9660 / ECMA-119) | All? | |
jbd2 | Generic filesystem journal-writing code (for ext4) | Squeeze | ||
jbd | Generic filesystem journal-writing code (for ext2/ext3) | All? | ||
jffs2 | MTD | The Journalling Flash File System, v2 | All? | |
minix | Minix native filesystem. (was used in Linux before ExtFS!) | All? | ||
msdos | I | MS-DOS filesystem support | All? | |
ncpfs | Netware NCP network protocol | All? | ||
nfs | N | Networks Filesystem | All? | |
ntfs(depreciated) | I | NTFS 1.2/3.x driver - Copyright (c) 2001-2007 Anton Altaparmakov | All? | |
ocfs2 | OCFS2 1.3.3 | All? | ||
omfs | OMFS (ReplayTV/Karma) Optimized MPEG Filesystem | >= Squeeze | ||
qnx4 | QNX (OS) Filesystem | All? | ||
romfs | ROM filesystem. See genromfs | <= Etch | ||
sysv | System V, V7 and Coherent and Xenix filesystems | All? | ||
ubifs | MTD | UBIFS - UBI File System | => Squeeze | |
udf | CD | Universal Disk Format Filesystem | All? | |
ufs | Unix filesystem, used in BSDs, SunOS, Nextstep, Openstep... | All? | ||
vfat | I | VFAT filesystem support | All? | |
zfs | The Z File System | => Stretch (DKMS) | ||
Features Legend :
Root: Suitable for system file system (like root and /usr...).
Interoperability: The filesystem is mostly implemented for Interoperability.
Distributed: file system.
Network Filesystem.
Sparsefile support
CD: Suitable for CD and/or DVD, etc.
MTD: Suitable for MTD devices.
Hints :
To list the FS types supported by your kernel, read its config file, run :
- To list the FS modules available in your kernel : To list the FS supported by your running kernel and currently loaded modules :
FUSE Filesystems
You can get the list of FS supported by through FUSE, by looking at the reverse dependencies on the package fuse-utils. At the time of writing :
Package name | Description | Distributions |
FUSE filesystem for APT source repositories | All | |
virtual filesystem to access archives, disk images, remote locations | All | |
implements a filesystem representing a live Beagle query | Sid | |
EncFS system tray applet for GNOME | All | |
filesystem to access FTP hosts based on FUSE and cURL | All | |
mount a WebDAV resource as a regular file system | All | |
encrypted virtual filesystem | All | |
virtual filesystem for flickr online photosharing service | All | |
user-space directory concatenation | ? | |
filesystem to mount WebDAV shares | All | |
File System in User Space - Module for ext2 | All | |
File System in User Space - Module for FAT | All | |
FUSE module to mount ISO filesystem images | All | |
File System in User Space - Module for ISO9660 | All | |
filesystem client based on the SMB file transfer protocol | All | |
clustered file-system | All | |
Use your GMail account as a filesystem | ? | |
filesystem to mount digital cameras | All | |
PAM module to automatically mount encfs filesystems on login | All | |
PAM module that can mount volumes for a user session | All | |
Fuse based remote filesystem for LTSP thin clients | All | |
file system for unifying several mount points into one | All | |
FUSE filesystem for Media Transfer Protocol devices | All | |
userspace filesystem client for MythTV | All | |
read/write NTFS driver for FUSE | >= Wheezy | |
ntfsprogs (depreciated) | tools for doing neat things in NTFS partitions from Linux | All |
mount filesystem of ObexFTP capable devices | All | |
Access EPOC device (Psion PDA) over a serial link | All | |
maps media files to an arbitrary directory structure | All | |
Read-Only Filesystem for FUSE | All | |
Full-featured file system for online data storage | All | |
filesystem client based on SSH File Transfer Protocol | All | |
View-OS in user space - ext2 module for UMFUSE | All | |
View-OS in user space - FAT module for UMFUSE | All | |
View-OS in user space - ISO9660 module for UMFUSE | All | |
Fuse implementation of unionfs | All | |
View and edit Wikipedia articles as if they were real files | All | |
implementation of Sun's ZFS filesystem in userspace | >=Squeeze |
Special file systems
Some sample use cases for special file systems:
allows mounting .vmdk (VMware) and .vdi(VirtualBox) image.
See also
Documents in the /usr/share/doc/linux-doc-2.6.26/Documentation/filesystems/ kernel module documentation (in package linux-doc-2.6 or above)
ToDo: Some modules provides 2 filesystems (for mount -t). e.g loading sysv provides sysv and v7 in /proc/filesystems.
CategorySystemAdministrationCategoryStorage
FUSE doesn't provide any filesystem it-self. see 'apt-cache rdepends fuse-utils' (1)
Data as file
Easily mount any kind of data as a virtual file and access it transparently from all your Windows applications. It can literally be anything: files from other locations, stored locally or remotely in the cloud... Creativity will be your limit.
Access Control
Working in user mode has several benefits and access control is one of them. You can have complex and custom access checks even with multiple security layers if you want to.
Be safe
Dokan takes care of the hard stuff and you never have to go deeper into kernel mode. This means you can develop your driver safely without having to fear BSOD at any test. Dokan code is available online since 2007. While people came and left the code remains alive thanks to the open source community.
Driver. Don't.
When you want to create a new file system on Windows you need to develop a file system driver. Developing a device driver that works in the kernel mode on Windows requires highly technical skills.
By using Dokan, you can create your own file systems very easily without writing device drivers. Dokan is similar to FUSE (Linux user mode file system) but works on Windows.
Fuse Ext4
User-mode API. As you like.
Dokan User-mode API provides functions to mount/unmount your driver and several callbacks to implement on your application to have a fully working user mode file system driver.
Additionally to the default provided C library, the API is also available for DotNet, Java, Delphi and Ruby.
FUSE Wrapper.
Dokan FUSE (Filesystem in Userspace) is a wrapper library that makes Dokan compatible with FUSE API. You simply need to rebuild your FUSE source code without changes with Cygwin/MinGW and link against the library to make it work on Windows. Now available by default in the main source repository and installers.
Projects. See it working.
Dokan is used in a variety of projects, a short list below.| Keybase | A cryptographically secure file mount using PGP key. |
|---|---|
| Nodrive | A confidential encrypted cloud storage. |
| DokanCloudFS | Access to different cloud storage services as virtual driver (OneDriver, Google Drive, MEGA, ...). |
| MooseFS | Fault-tolerant, POSIX-compliant, network distributed filesystem |
| Atmo O | Inter & Intra document aliasing |
| Kortex Mod Manager | Mod manager for various PC games. |
| yasfw | Yet Another SSHFS for Windows |
| Shaman.Dokan.Warc | Mounts WARC files (web archives) as FS. |
| Shaman.Dokan.Archive | Mounts 7zip/ZIP/RAR files as FS. |
| fuse-nfs-crossbuild-scripts | fuse-nfs for windows using dokany. |
| Dokan SSHFS | SSH File System |
| MLVFS | Magic Lantern Video File System |
| Win-SSHFS | SSH with SSH.NET File System |
| RedFS | Single File System |
| encfs4win | Encryption File System |
| Opendedup CDFS | Deduplication Based File System |
| Dokan NFC | RFID / NFC File System |
| Ninefs | 9p File System |
| WinUnionFS | UnionFS-like File System |
| MSSQLFS | MS SQL File System |
| PeoneFS | Pseudo Encrypted and Obfuscated File System |
| DiscUtils | Image/Partition mounter using DiscUtils |
| ZFS-Win | ZFS File System |
| FtpUse | FTP File System |
| ChunkFS | Chunked File System |
| CueMounter | Cue File System |
| SrcDemo² | Render smoother Source Engine videos, faster |
| xbox-iso-vfs | Xbox ISO File System |
| ... | ... |
Frequently Asked Questions
It has been maintained from 2011 to 2014 by the community with different fork.
Since 2014, the project is highly maintained by Adrien J. and Maxime C. with the fork Dokany and gracefully code signed by the company ISLOG.
Support Us. Thank you.
Maintaining a Windows driver and its associated libraries requires time and specific knowledge (ok, as always). We focus on stability and improvement but any help (code contribution, testing, issues resolving ...) is highly appreciated.
Dokan reviving through Dokany fork is a personal initiative and we don't get money from it. If you're making a business based on Dokan or just enjoy it, please consider to support the real current developers using bounties. Alternatively you can also directly use Github Sponsor button. Be fair.
Fuse Ext4
They already trust and sponsor Us.
Fuse Ext4 Linux
Big thanks to them !